Why does my dog smell of fish?
Typical Reasons Behind the Fishy Smell in Dogs

- Anal Gland Issues
Anal glands located near the dog’s anus can become impacted or infected, leading to a fishy odor.
- Skin Infections
Bacterial or fungal skin infections can produce a strong odor reminiscent of fish.
- Dietary Factors
Certain fish-based diets or fish oil supplements can sometimes cause a fishy smell in a dog’s coat or breath.
- Ear Infections
Infections in the ears can produce a foul odor that may be reminiscent of fish.
Less Common Causes of Fishy Odor in Dogs
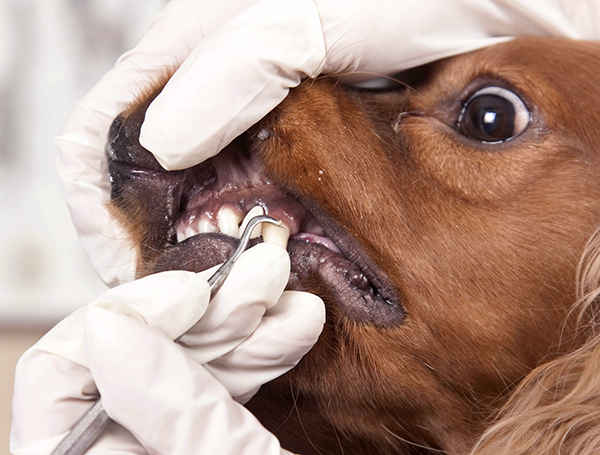
- Oral Health Problems
Gum disease or tooth decay can cause halitosis reminiscent of a fishy odor.
- Seborrhea
This skin condition can cause an overproduction of oils, leading to a strong odor resembling fish.
- Liver or Kidney Disease
Certain metabolic disorders can cause a buildup of waste products in the body, leading to an unusual smell on the breath or skin.
- Anal Fistulas
These abnormal connections between the anal glands and the skin can cause chronic infection and a fishy odor.
Interesting Facts about Fishy Odor in Dogs

- Scent Glands
Dogs have scent glands not only in their anal area but also throughout their bodies, contributing to their unique odor profile.
- Species Variability
Just like humans, individual dogs can have different natural body odors, influenced by factors diet, breed, and overall health.
- Self-Cleaning Mechanisms
Dogs groom themselves by licking, which can sometimes spread odor-causing substances across their fur.
- Hygiene Importance
Regular grooming, including cleaning the ears and anal area, can help prevent or reduce fishy odors in dogs.
Understanding these potential causes and intriguing facts can assist in identifying and addressing the source of your dog’s fishy odor.












