Why does my coolant reservoir keeps emptying?
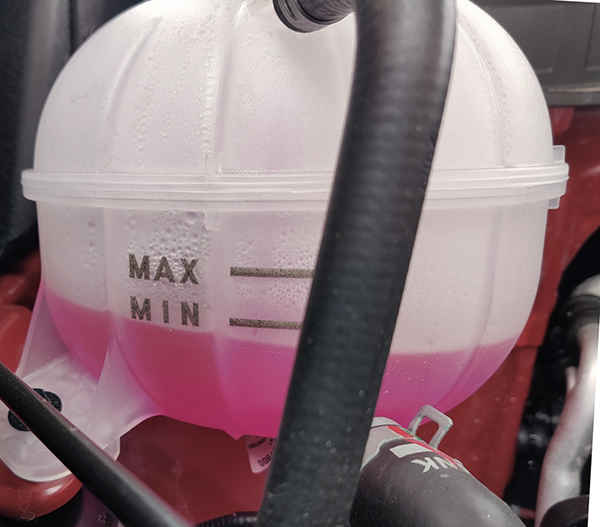

Reasons for Coolant Reservoir Emptying:
Coolant Leak
- Description: Coolant leaks can occur due to various reasons – example: worn-out hoses, loose connections, or a damaged radiator.
- Impact: Continuous leakage can lead to a decrease in coolant levels in the reservoir, eventually causing engine overheating and potential damage.
Internal Engine Leak
- Description: Internal engine leaks, example: a blown head gasket or a cracked engine block, can allow coolant to mix with oil or leak into combustion chambers, leading to its consumption or evaporation.
- Impact: These leaks are often more severe and may require professional inspection and repair to prevent further damage to the engine.
Evaporation
- Description: In hot climates or due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures, coolant can evaporate from the reservoir, causing a decrease in its level.
- Impact: While evaporation alone might not indicate a serious issue, it’s essential to regularly monitor coolant levels and refill as needed to prevent engine overheating.
Coolant System Bleeding
- Description: Improper bleeding of the coolant system after maintenance or repairs can lead to air pockets within the system, causing fluctuations in coolant levels in the reservoir.
- Impact: Air pockets can disrupt the flow of coolant, leading to inefficient cooling and potential overheating of the engine.
Overflow Due to Overfilling
- Description: Overfilling the coolant reservoir beyond its maximum capacity can cause excess coolant to overflow, appearing as if the reservoir is constantly emptying.
- Impact: Overflowing coolant can result in wastage and potential spillage, necessitating cleanup and proper level adjustment.
What to Do?

- Inspect for Leaks
Regularly check for visible leaks around hoses, connections, and the radiator. Repair any leaks promptly to prevent coolant loss.
- Check Internal Leaks
If suspecting internal engine leaks, perform a comprehensive inspection or consult a professional mechanic for diagnosis and repair.
- Monitor Coolant Levels
Keep a close eye on coolant levels in the reservoir and refill as needed to maintain optimal engine cooling.
- Properly Bleed Coolant System
Ensure proper bleeding of the coolant system after maintenance or repairs to eliminate air pockets and maintain consistent coolant levels.
- Avoid Overfilling
Refill coolant to the recommended level and avoid overfilling the reservoir to prevent unnecessary overflow.
Operational Car Facts

Ethylene Glycol: Most modern coolants contain ethylene glycol, which has a high boiling point and low freezing point, making it ideal for use in automotive cooling systems.
Antifreeze Properties: Coolants not only prevent engines from freezing in cold temperatures but also provide corrosion protection and aid in heat transfer, enhancing engine performance.
Coolant Recycling: Many automotive service centers recycle used coolant to minimize environmental impact and reduce waste generation. The recycled coolant undergoes purification processes before reuse.