Why can’t electric cars charge themselves?
Reasons:
Battery Technology Constraints
Electric vehicle (EV) batteries are based on lithium-ion technology, which requires external charging. These batteries store energy chemically and do not have inherent mechanisms to generate electricity internally.
Example: A Tesla Model 3’s battery pack is designed to store energy for propulsion but cannot generate electricity by itself.
Physical and Thermodynamic Limitations
According to the laws of thermodynamics, energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another. Self-charging would require violating these fundamental laws, which dictate that energy inputs must come from an external source.
Example: Just like how a smartphone cannot recharge its battery by itself without a charger, electric cars require an external power source.
Efficiency and Practicality Challenges
Even if hypothetical methods of self-charging were developed, the efficiency and practicality of such systems would be questionable. Any energy generated by the car’s movement or environment (example: solar panels on the car’s surface) would not be sufficient to offset the energy demands of driving.
Example: Solar panels on roofs of cars can generate some electricity, but the amount is minimal compared to the energy required for typical driving distances.
What Can Be Done?

To enhance the usability and efficiency of electric vehicles:
- Advancements in Battery Technology
Continued research into improving battery energy density and charging speeds can extend range and reduce charging times.
- Infrastructure Expansion
Increasing the number and accessibility of charging stations to alleviate range anxiety and support longer trips.
- Innovative Charging Solutions
Exploring technologies like wireless charging and rapid charging to make recharging more convenient and faster.
Interesting Information

Regenerative Braking: Electric vehicles can recover energy during braking by converting kinetic energy into stored electrical energy, improving efficiency and extending range.
Future Possibilities: Researchers are exploring concepts like wireless charging roads that could potentially charge EVs while they drive, though these technologies are still in early stages of development.
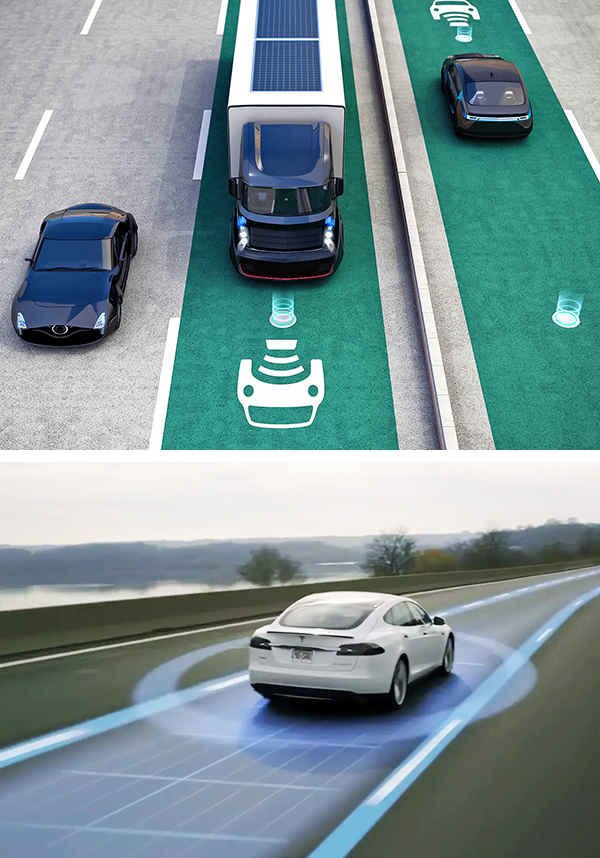

Understanding these limitations and ongoing innovations helps in appreciating the current capabilities and future potential of electric vehicles in transportation.
Here are some recent news updates on electric vehicles

Global Surge in Electric Vehicle Sales:
Throughout 2024, there has been a significant increase in electric vehicle sales worldwide, marking record numbers in several countries including the USA, China, and various European nations.
Technological Advancements in Battery Technology:
Recent breakthroughs in battery technology have focused on improving energy density and charging speeds, promising longer ranges and faster charging times for electric vehicles.
Government Initiatives and Policies:
Many governments are implementing aggressive policies to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles, including incentives for consumers, investments in charging infrastructure, and stricter emissions regulations.
Automaker Commitments to Electrification:
Major automakers continue to announce ambitious plans to electrify their vehicle fleets, with commitments to phase out internal combustion engines in favor of electric powertrains over the next decade.
Innovation in Charging Solutions:
Innovations in charging technology, example: ultra-fast chargers and wireless charging systems, are being developed to enhance convenience and reduce the charging time for electric vehicle users.
These developments highlight the dynamic growth and innovation within the electric vehicle industry as it strives towards a more sustainable future for transportation.